As negotiations in advance of the 15th Convention of the Parties to the Convention on Organic Variety (COP-15) acquire location, intercontinental study has quantified the influence of human usage on species extinction risk.
Close to 1 million species previously face extinction, many in just many years, according to the new Intergovernmental Science-Plan System on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) evaluation report.
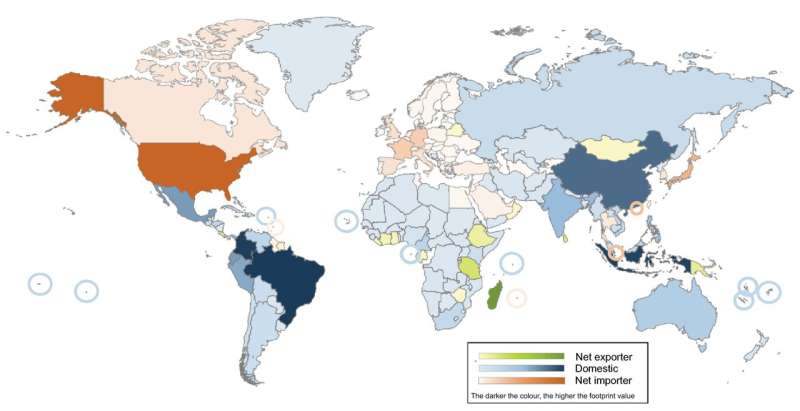
Spanning extra than 5,000 species in 188 nations, the study finds usage in Europe, North The usa, and East Asia (these as Japan and South Korea) mostly drives species extinction chance in other nations around the world. Afflicted species consist of the Nombre de Dios Streamside Frog in Honduras and the Malagasy Large Jumping Rat in Madagascar.
Printed in Scientific Studies, the research is led by Ms Amanda Irwin at the College of Sydney’s Integrated Sustainability Examination research team and is co-authored by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) main scientist Dr. Thomas Brooks and chief economist Dr. Juha Siikamäki.
The authors liken the biodiversity crisis to the local weather one, albeit with much less publicity. “These crises are happening in parallel,” Ms Irwin explained. “The forthcoming COP-15 will with any luck , raise the profile of the other human-driven all-natural crisis of our generation—irreparable biodiversity loss—and our conclusions can deliver useful insights into the job that worldwide use performs as 1 of the drivers of this decline.”
Key results:
- Use in 76 countries, concentrated in Europe, North The united states, and East Asia, primarily drives extinction chance in other countries.
- In 16 nations around the world, concentrated in Africa, this extinction-risk footprint is driven by offshore usage.
- In 96 countries—around half of all those studied—domestic intake is the greatest driver of the extinction-threat footprint.
- Intercontinental trade drives 29.5 % of the world wide extinction-threat footprint.
- Intake of solutions and solutions from the meals, beverage and agriculture sectors is the biggest driver of intake-pushed extinction chance, alongside one another constituting 39 % of the world wide extinction-chance footprint, followed by consumption of merchandise and products and services from the design sector (16 per cent).
Ph.D. prospect Ms Irwin reported: “The complexity of economic interactions in our globalized entire world implies that the acquire of a espresso in Sydney could lead to biodiversity loss in Honduras. The alternatives we make each and every day have an impact on the organic entire world, even if we do not see this impression.”
“Almost everything that we take in has been derived from the organic earth, with uncooked components transformed into finished merchandise as a result of a myriad of source chain transactions. These transactions generally have a immediate effect on species.”
Co-author, IUCN main economist Dr. Juha Siikamäki notes: “This perception into how prevalently usage styles influence biodiversity reduction across the world is essential to advise ongoing intercontinental negotiations for character, which includes the 15th Convention of the Parties to the Conference on Biological Diversity, which aims to finalize the article-2020 world biodiversity framework later on this year.
“The getting from this research that about 30 p.c of the global extinction-threat footprint is embedded in intercontinental trade underlines the have to have to contemplate the tasks of distinct nations and all actors, such as funding of conservation, not only in the context of their countrywide boundaries but extending to their impacts internationally.”
Co-writer, Affiliate Professor Arne Geschke from the Built-in Sustainability Assessment research group at the College of Sydney explained: “The pursuits which threaten species in a presented site are generally induced by usage patterns in significantly-absent areas, that means that neighborhood interventions may possibly be inadequate.
“Suitable interventions to tackle extinction danger in Madagascar, for instance, exactly where 66 per cent of the extinction-threat footprint is exported, ought to be various from those people carried out in Colombia, the place 93 p.c of the extinction-danger footprint is generated by domestic use.”
About the research
Using information available in IUCN’s Red Listing of Threatened Species, the authors launched the non-normalized Species Menace Abatement and Restoration (nSTAR) metric as a evaluate of extinction danger.
They then applied the methodology extensively-utilised to quantify carbon footprints—of which the Integrated Sustainability Analysis analysis team is a globe leader—to link this extinction chance to world-wide usage designs making use of the global provide chain database Eora.
An extinction-risk footprint was calculated by species, by financial sector, for 188 nations.
Co-creator Associate Professor Arne Geschke beforehand co-wrote a Scientific Reviews paper that demonstrated global trade is a key driver of biodiversity threats.
This new paper is a collaboration concerning the University of Sydney, IUCN, Newcastle University (United kingdom) and the International Institute for Sustainability in Brazil.
Recently explained species have higher extinction threat
Amanda Irwin et al, Quantifying and categorising nationwide extinction-threat footprints, Scientific Stories (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-09827-
College of Sydney
Quotation:
Your early morning coffee could hasten species’ extinction (2022, April 13)
retrieved 7 July 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-04-early morning-espresso-hasten-species-extinction.html
This doc is subject matter to copyright. Aside from any honest working for the function of non-public examine or study, no
part might be reproduced without having the created permission. The content material is supplied for information purposes only.

More Stories
Famous Matcha Cafe From Japan Opens In Singapore At Clarke Quay
A fan of black coffee and dark chocolate? It’s in your genes, a new study says
Your favorite Coffee reveals these personality traits